The leaded shield is here in a closed position

The radiation symbol is in fact on the another shield. On the right is the meter for the Geiger counter.
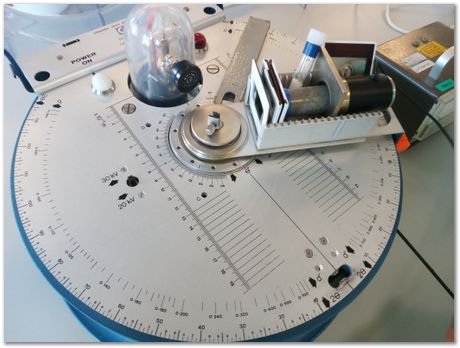
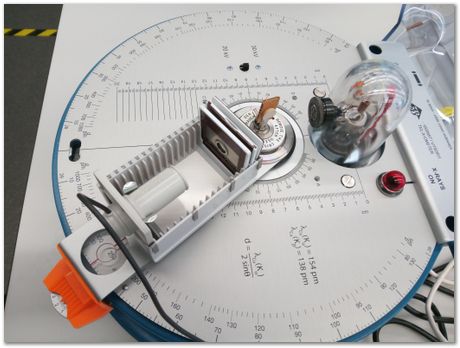
Not properly set up, but there are collimators and nickel filter in the slide holder that also retains the Geiger counter.
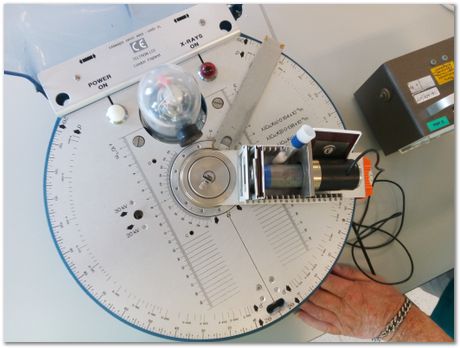
The Ni filter is to cut some of the K-beta Cu X-rays.
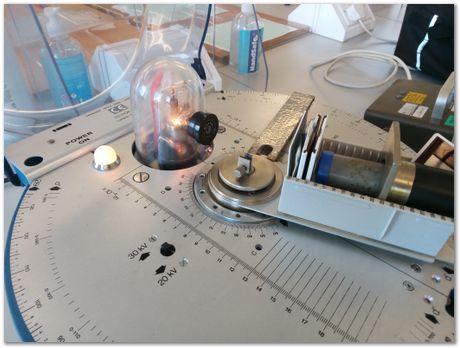
Although the light is on, the X-rays are not because the shield is not in position

III
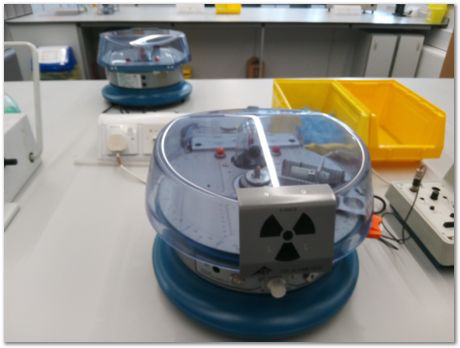
Bought two of these for the practical class.

The machines require these keys to operate.

III

III

III

III
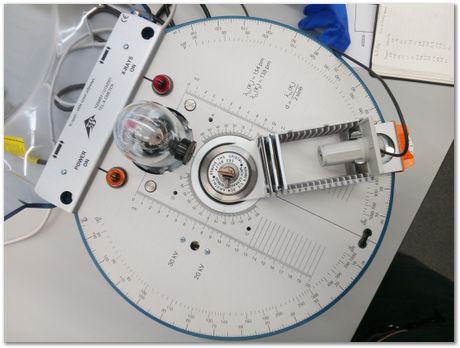
The counter is rotated about the centre to measure counts versus two-theta
III

This is something else which is in my wish list, but not yet constructed at QMUL because the polarisers did not arrive on time.

I wish to demonstrate phase transformations in polymers as a function of stress and strain, by stretching them between crossed polars. Any development of crystallinity will transmit light, otherwise dark.