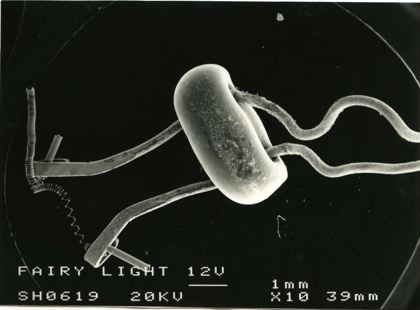

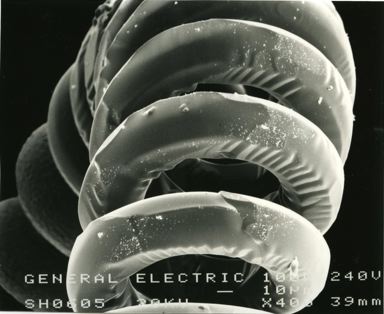
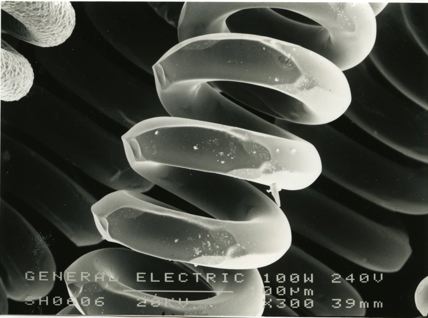
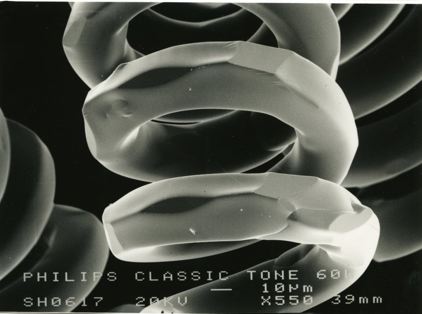
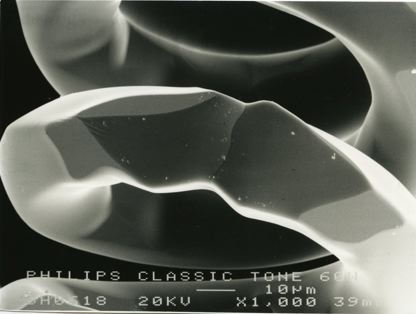
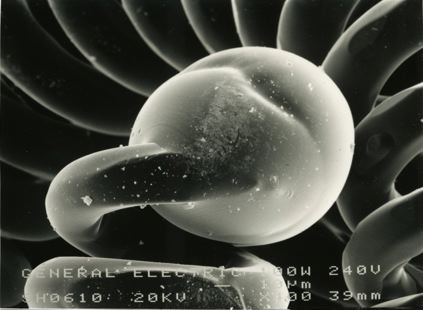
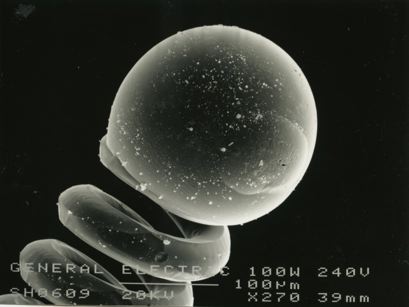
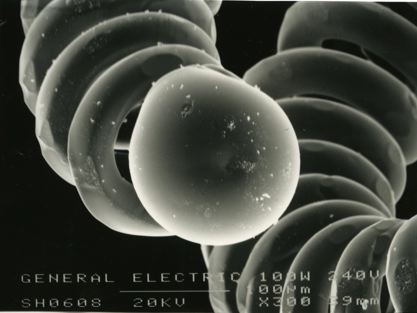
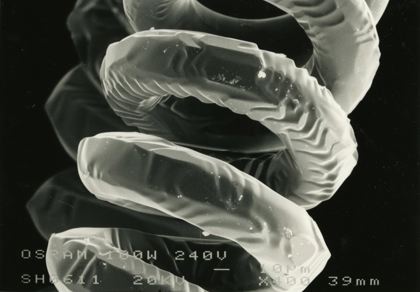

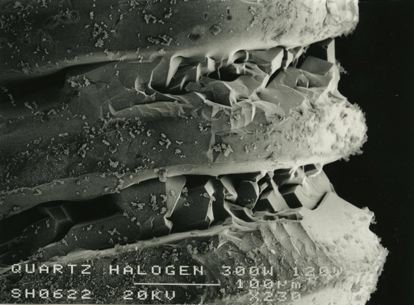
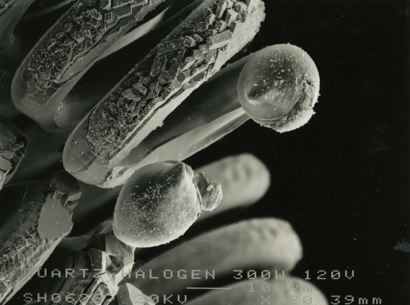
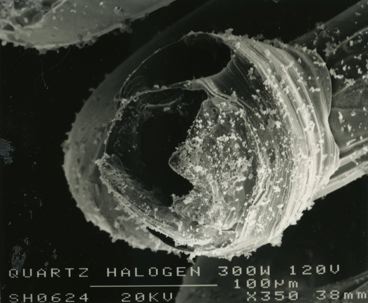
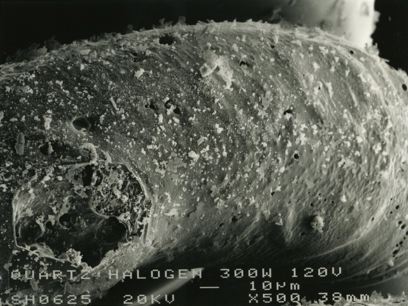
These micrographs were given to me as part of my undergraduate project at The University of Sheffield: Case Study on Tungsten Filament Lamps. The report includes a discussion of the manufacture of tungsten filament lamps, some of the physics involved and alternative light sources.
The project was taught with great enthusiasm by Prof. G. W. Greenwood.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Images courtesy of P. D. Bhadeshia.
Wolframite, (Fe,Mn)WO4, has a monoclinic lattice in which a=0.477 nm, b=0.573 nm, c=0.498 nm, β=90.2o, space group P2/c. It is a valuable source of tungsten that can be used in armaments.
The Cligga Mine & Nobels Munitions Factory initially was focused on making explosives but during the second war, tungsten mining became important. This enabled armour plated with tungsten and also shells that could penetrate ordinary armour, presumably as kinetic-energy projectiles given the density of tungsten at 19.3 g cm-3.
This is one of the settling tanks at Cligga Head Wolframite mine. The purpose is to allow sedimentation in order to separate out relatively clear water from mineral spoils.
 4th edition, 2017 |
 Free download |
 Free download |
 Published 2022 |
 Available |
 Available |
| PT Group Home | Materials Algorithms |