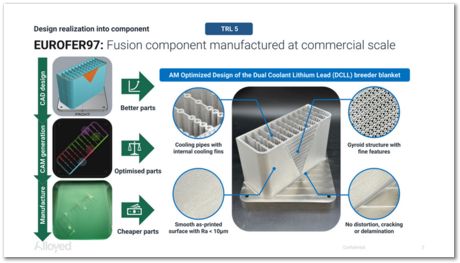
The complex design can only be achieved using additive manufacture.

Shaumik Lenka, Dhairyasheel Patil at the U.K. Atomic Energy Authority, exhibiting their component made of Eurofer97.
Quite remarkable and convoluted channels.
![[Queen Mary University of London]](https://www.phase-trans.msm.cam.ac.uk/QMUL.png)
This achievement by Shaumik Lenka, Dhairyasheel Patil and Shanoob Balachandran, from Alloyed Ltd. is in the context of future fusion reactors. A dual coolant lead-lithium breeder blanket is intended for use in magnetic confinement fusion, such as in Tokamak designs.
Tritium is a key fuel for fusion reactions, and the blanket is designed to breed tritium from lithium. The lead-lithium mixture facilitates this process, as lithium can react with neutrons produced during fusion to generate tritium.
The blanket absorbs heat generated from the fusion reactions and the neutron interactions. This heat can then be used in principle to produce steam and drive turbines for electricity generation.
The blanket also acts as a radiation shield, protecting the reactor components and the environment from harmful neutron radiation.
There are two different coolants in the system, one of which is a liquid metal (like lead or lead-lithium) that efficiently transfers heat and absorbs neutrons, while the other coolant might be a gas or another liquid that circulates to remove heat from the blanket and transfer it to a power generation system.
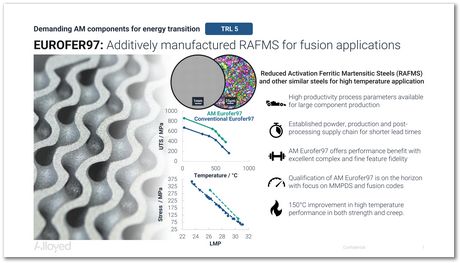
The component illustrated here, fabricated using laser powder bed fusion as the additive manufacturing method, is made using a reduced activation steel Eurofer97. This typically has Fe-0.1C-9Cr-1.1W-0.4Mn-0.12Ta-0.03N wt%, avoiding any solutes that on irradiation would have long half-lives. This is why it is known as a reduced activation steel.
 5th edition published 2024 |
 Free download |
 Free download |
 Available |
 Free download Published 2021 |
 Free download |
 Free download |
 Published 2025 |
| PT Group Home | Materials Algorithms |