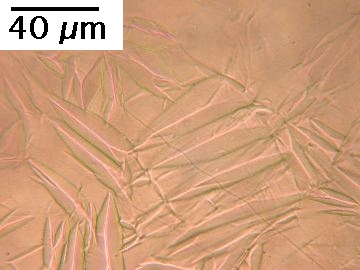
Martensitic transformation causes not only a change in crystal structure, but also a permanent deformation. If a sample of austenite is metallographically polished and then transformed to martensite, surface upheavals of the kind illustrated below are created. Any scratch that existed on the surface of the austenite becomes deflected by martensitic transformation. The scratch changes orientation due to the shear associated with martensite, but maintains continuity across the martensite-austenite interface. This is because the interface between martensite and austenite maintains sufficient coherency. Such coherency is necessary for any diffusionless transformation.
The images are all taken from an unetched sample prepared in the manner described above, using an ordinary optical microscope.
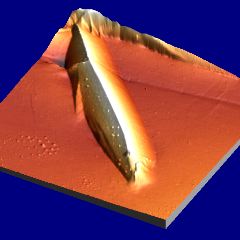
Isolated plates of martensite characterised using atomic force microscopy. The sample details are as for the optical micrographs described above.
Martensite: deformation caused by martensitic transformation. Fe-0.31C-30.5Ni wt% |

Martensite: deformation caused by martensitic transformation. Fe-0.31C-30.5Ni wt% |

Martensite: deformation caused by martensitic transformation. Fe-0.31C-30.5Ni wt% |
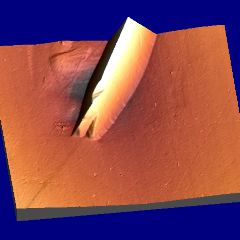
Martensite: deformation caused by martensitic transformation. Fe-0.31C-30.5Ni wt% |

Martensite: deformation caused by martensitic transformation. Fe-0.31C-30.5Ni wt% |
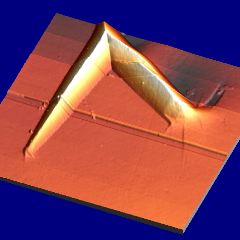
Martensite: deformation caused by martensitic transformation. Fe-0.31C-30.5Ni wt% |

Martensite: deformation caused by martensitic transformation. Fe-0.31C-30.5Ni wt% |
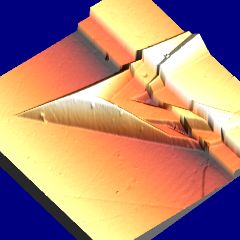
Martensite: deformation caused by martensitic transformation. Fe-0.31C-30.5Ni wt% |

Martensite: deformation caused by martensitic transformation. Fe-0.31C-30.5Ni wt% |
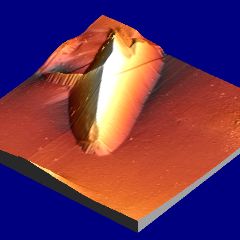
Martensite: deformation caused by martensitic transformation. Fe-0.31C-30.5Ni wt% |

Martensite: deformation caused by martensitic transformation. Fe-0.31C-30.5Ni wt% |
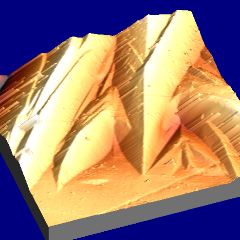
Martensite: deformation caused by martensitic transformation. Fe-0.31C-30.5Ni wt% |

Martensite: deformation caused by martensitic transformation. Fe-0.31C-30.5Ni wt% |
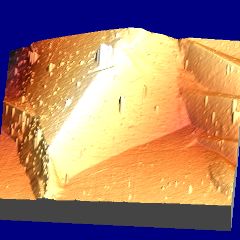
Martensite: deformation caused by martensitic transformation. Fe-0.31C-30.5Ni wt% |
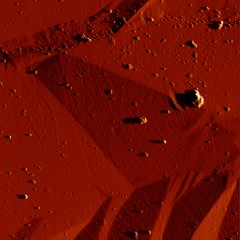
Martensite: deformation caused by martensitic transformation. Fe-0.31C-30.5Ni wt% |