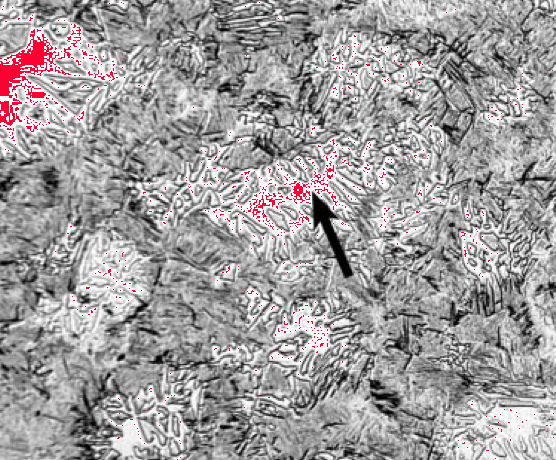
A steel has recently been designed to benefit from the deformation induced transformation of retained austenite present in association with bainitic ferrite. It has as its major microstructural component, dendrites of δ-ferrite introduced during solidification. The δ-ferrite replaces the allotriomorphic ferrite present in conventional alloys of this kind. The authors examine here the stability of this δ-ferrite during heating into a temperature range typical of hot rolling conditions. It is found that contrary to expectations from calculated phase diagrams, the steel becomes fully austenitic under these conditions and that a better balance of ferrite promoting solutes is necessary in order to stabilise the dendritic structure. New alloys are designed for this purpose and are found suitable for hot rolling in the two-phase field over the temperature range 900-1200°C.
Materials Science and Technology, 27 (2011) 525-529.

| Synchrotron | Stainless welds | Extraordinary | Commentary | Problems |
| Residual stress | Aluminium | Tired steel | Bearings | Intervention |
| δ-TRIP | Metallography | Mechanicallly Alloyed | Extraordinary | Retained Austenite |
| PT Group Home | Materials Algorithms |