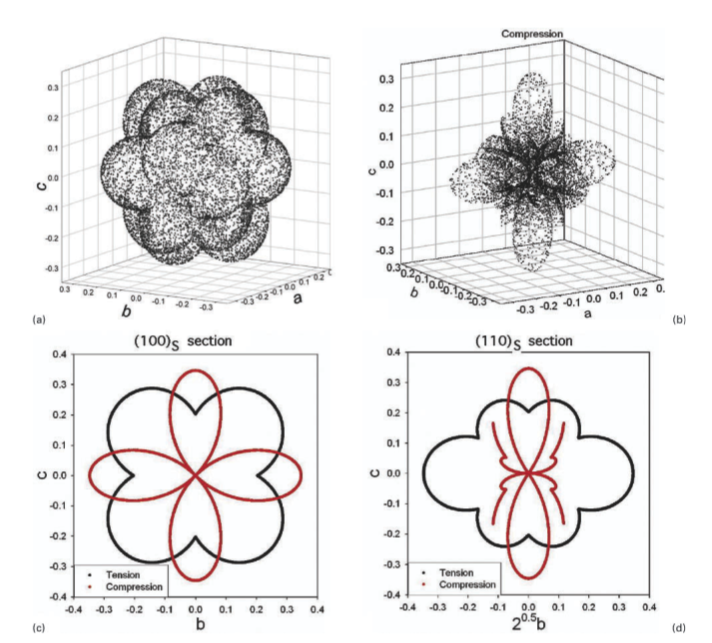
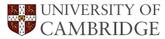
Twinning induced plasticity steels are austenitic alloys in which mechanical twinning is a prominent deformation mode, and which exhibit exceptional combinations of ductility, work hardening and ultimate strength. The authors develop in the present paper a crystallographic theory to enable the quantitative investigation of the role of mechanical twinning in enhancing the properties of these alloys. It is found that the twinning strain itself makes a significant though small contribution to the total elongation and that other mechanisms must therefore be at play in determining the overall deformation behaviour.
Materials Science and Technology 24 (2008) 969-973.

| Superalloys | Titanium | Bainite | Martensite | Widmanstätten ferrite |
| Cast iron | Welding | Allotriomorphic ferrite | Movies | Slides |
| Neural Networks | Creep | Mechanicallly Alloyed | Theses | Retained Austenite |
| PT Group Home | Materials Algorithms |